Numbers, Strings, Operators
Class objectives
Syntax table
| Defines the width of the pen. Patameter - integer is a value type of int | |
| is a conditional statement. | |
| is a loop statement in which operations repeat itself for a limited amount of time |
Number
What is Number?
Numbers in Python are the same as the numbers you have learnt in math class. We have four mathmatical operators.
How to define a number variable?
# num is the name, 17 is the value, = means assign value 17 to variable num
num = 17
print(num)
How to define multiple number variables?
# num01, num02 and num03 are the names. 23, 46 and 78 are the values, = means assign values 23, 46 and 78 to variables num01, num02 and num03.
num01, num02, num03 = 23, 46, 78
print(num01, num02, num03)
Operators
- addition +
- subtraction -
- multiplication *
- division /
- floor division //
- remainder %
- assign sign =
- equal sign ==
num01, num02, num03 = 23, 46, 78
add = num01 + num02
sub = num02 - num01
mul = num01 * mul03
divi = num02 / num01
print('Addition: ' + int(add))
print('subtraction: ' + int(sub))
print('Multiplication: ' + int(mul))
print('Division: ' + int(divi))
String
What is String?
String is the text we print in console or in turtle screen.
How to define a String variable?
# string is the name, 'Hello, Python' is the value, = means assign value 'Hello, Python' to variable string
string = 'Hello, Python'
print(string)
How to define multiple String variables?
# string01, string02 and string03 are the names. 'My name', " is", ' Alim' and '7' are the values, = means assign values 'My name', " is", ' Alim' and '7' to variables string01, string02 and num03.
string01, string02, string03, string04 = 'My name', " is", ' Alim', '7'
print(string01, string02, string03, string04)
How to link strings together?
string01, string02, string03, string04 = 'My name', " is", ' Alim', '7'
print(string01 + string02 + string03)
How to convert a number to string and back?
For example: 'Addition: ' and add are different data types. In Python, unable to add two different data types unless one of which is converted to the type of another. int() is a Python function converts String to Number. str() is a Python function converts Number to String.
Practice them in turtle
How to print a String in turtle?
We need write() function to print a String in turtle. For example:
from turtle import *
write("Python is fun!", align='center', font=('Arial', 38, 'bold'))
How to practice Number in turtle?
It’s easy to do a calculation and present the result on turtle screen. For example:
write("{0} + {1} = {2}".format(5, 7, 5 + 7), align="center", font=("Arial", 48, "bold"))
penup()
goto(0, 200)
write("{0} - {1} = {2}".format(5, 7, 5 - 7), align="center", font=("Arial", 48, "bold"))
penup()
goto(0, 100)
write("{0} * {1} = {2}".format(5, 7, 5 * 7), align="center", font=("Arial", 48, "bold"))
penup()
goto(0, -100)
write("{0} / {1} = {2}".format(5, 7, 5 / 7), align="center", font=("Arial", 48, "bold"))
penup()
goto(0, -200)
write("{0} // {1} = {2}".format(5, 7, 5 // 7), align="center", font=("Arial", 48, "bold"))
penup()
goto(0, -300)
done()
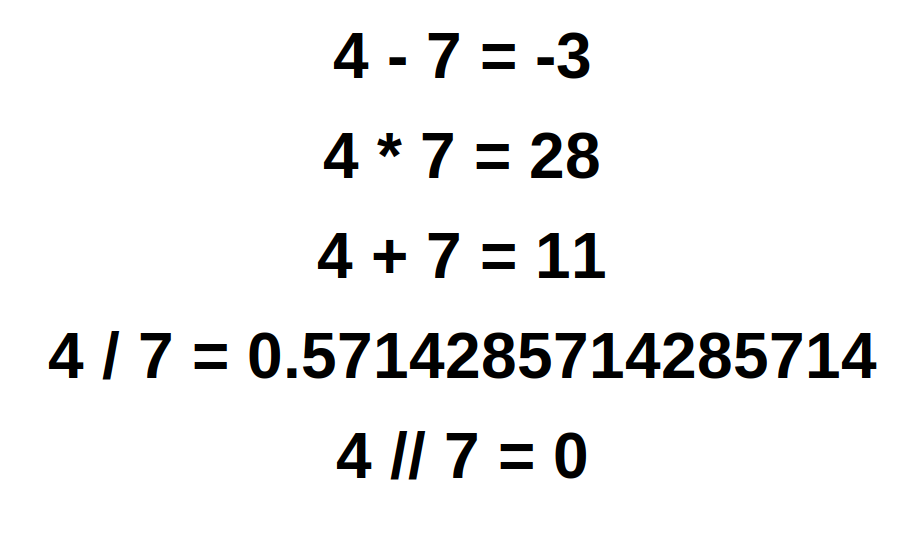
How to practice List in turtle?
Assume we have random colors in a list, paint each shape in a different color. For example:
square = 4
triangle = 3
red, green, yellow = 'red', 'green', 'yellow'
# Following is how to define a function
# def is a suffix indicates define a function. draw is the name of function. sides is the parameter. We'll talk about more details in following classes.
def draw(sides):
width(30)
if sides == square:
color(green)
elif sides == triangle:
color(yellow)
for each_side in range(sides):
forward(100)
right(360/sides)
done()
# Following is how to call a function
draw(4)
if draw(4)
if draw(3)
Homework: Draw shapes in different color
Input
Given a function with a parameter of sides. If sides is even, draw the shape in red color. If sides is odd, draw the shape in green color.
For example
def draw_even_odd(sides):
Output
if draw_even_odd(8)
if draw_even_odd(5)